Blog Author: Archita Khaire
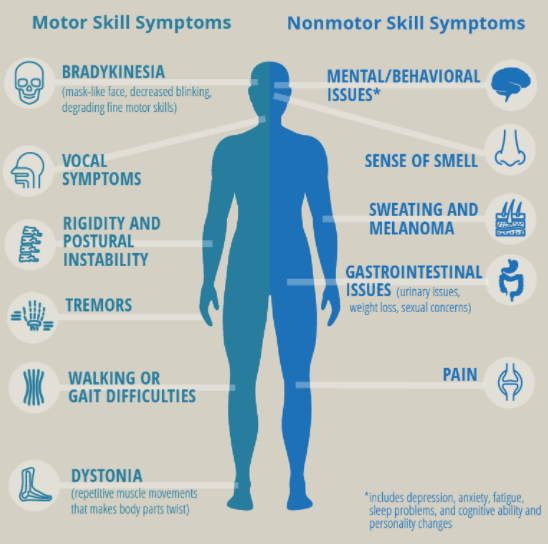
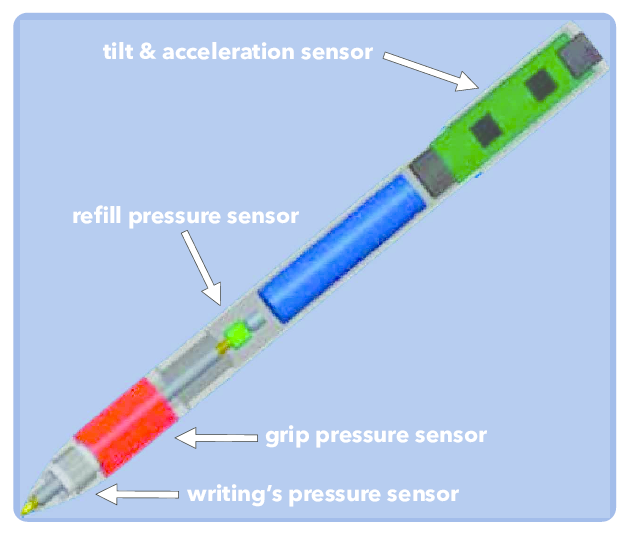
Currently, there is no cure for Parkinson's disease. It doesn't always affect how long you live but has a severely negative impact on the quality of life of patients and their caregivers. Early detection of PD can improve the symptoms dramatically. Image Credit: https://www.pcori.org/research-results/pcori-stories/improving-life-women-parkinsons-disease Early Detection of PD using AI Multiple early signs can indicate the onset of Parkinson's disease. Health data collected around these signs are used to build machine-learning algorithms that can predict the PD. 1. Speech impairments like dysphonia (defective use of the voice), hypophonia (reduced volume), monotone (reduced pitch range), and dysarthria (difficulty with the articulation of sounds or syllables) are used to detect PD. UCI Machine Learning Repository: Parkinson's Telemonitoring Data Set was created by Athanasios Tsanas and Max Little of the University of Oxford in collaboration with ten medical centers in the US and Intel Corporation. They developed the telemonitoring device to record speech signals.
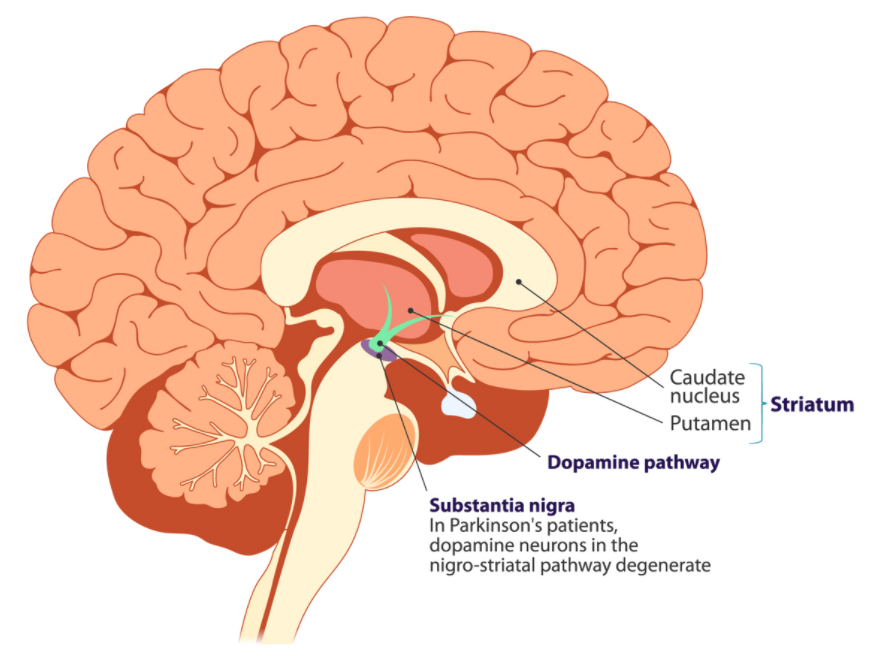
Image Credit: DOI:10.1109/SIBGRAPI.2016.054 3. Difficulty in walking is another sign of growing Parkinson's disease. Deep learning algorithms are used in Gait analysis to classify the movement properties into two classes, PD and non-PD, using features such as imbalance, frequency of falls, and a few other factors. 4. Researchers are attempting to detect PD using human olfactory data. In patients with OD, loss of smell starts many years early before the onset of motor skill symptoms. There is potential to diagnose PD much early with this method. Leveraging AI to treat PD Parkinson's is caused by the death of dopamine-producing nerve cells. Scientists at Stanford school of medicine identified Miro1, a mitochondrial protein that resists the removal of damaged cells. They analyzed millions of drugs using AI to identify a compound that could bind with Miro and enhance the cell mechanism to remove damaged nerve cells. Researchers at John Hopkins have identified the glucagon-like peptide receptor or GLP1 receptor as a potential receptor for slowing down PD. They are leveraging AI to check if diabetes drugs could be used to prevent neurological cell deaths. References:
Comments are closed.
|
Page HitsAuthorArchita Archives
January 2023
Categories |

 RSS Feed
RSS Feed