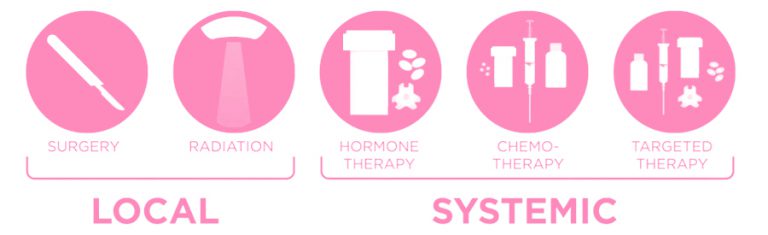
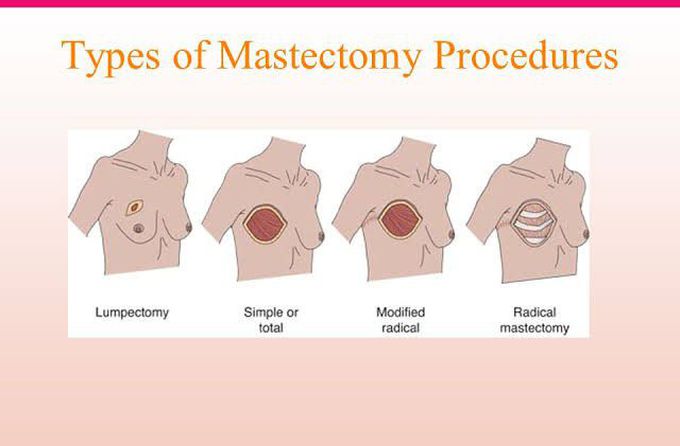
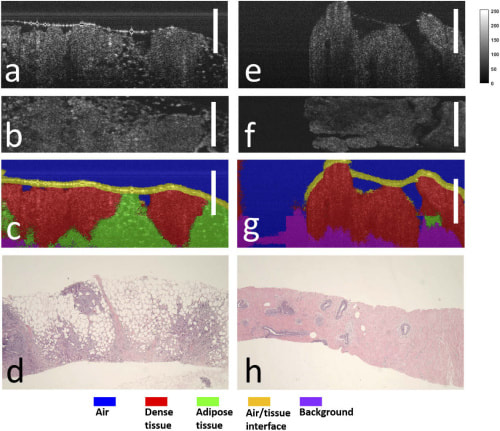
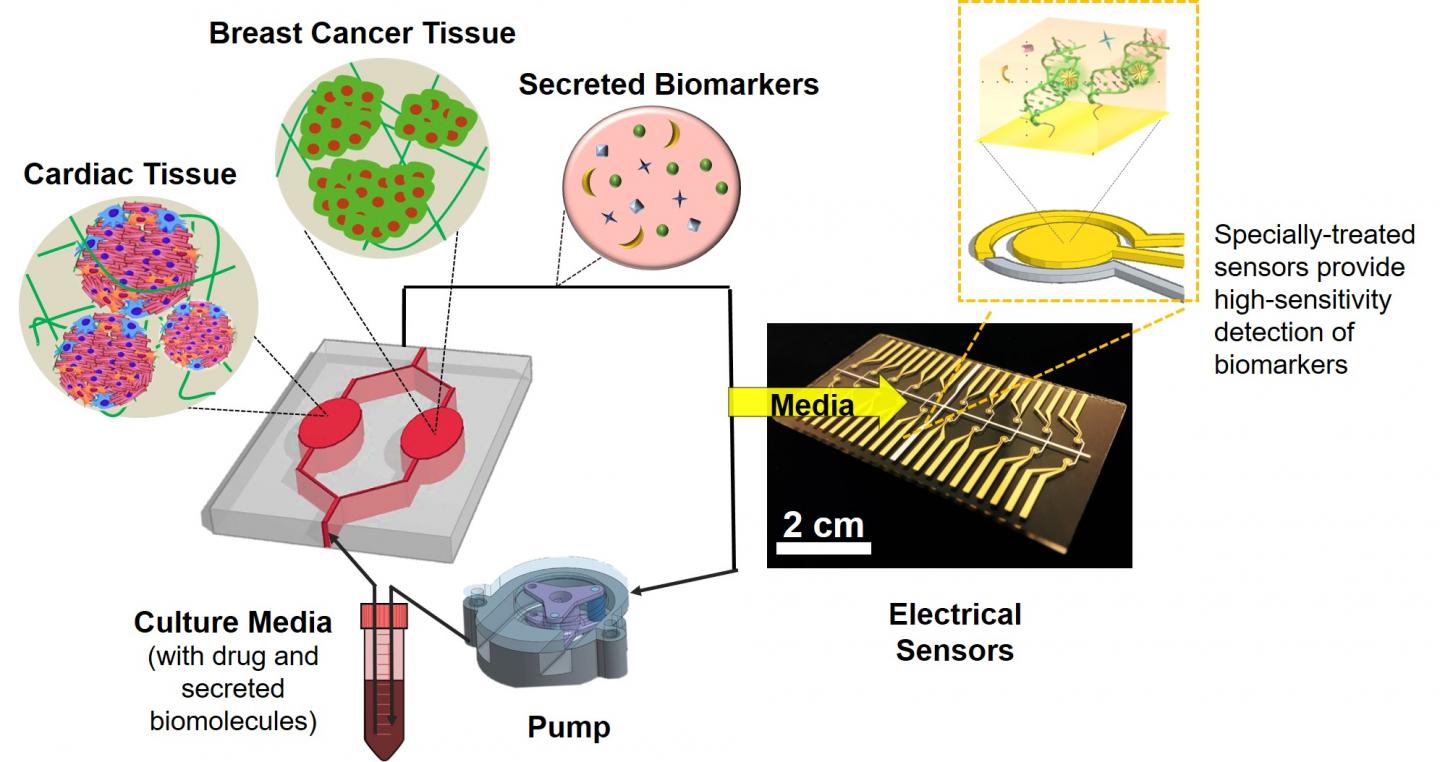
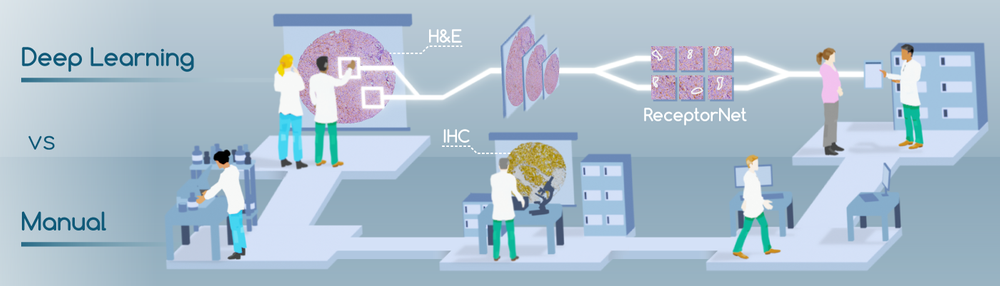
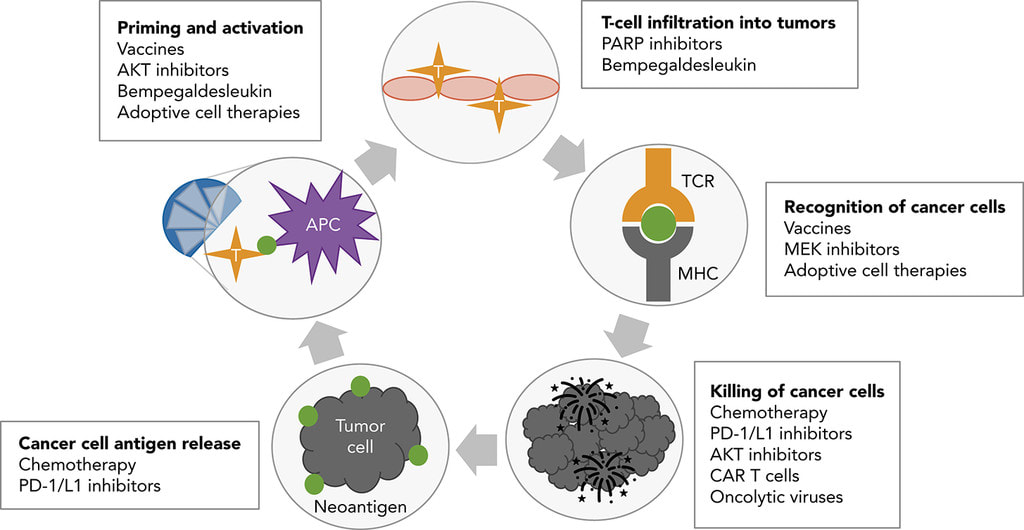
Blog Author: Archita KhaireBreast cancer treatment depends on the stage and type of breast cancer. In localized cancer, patients receive breast-conserving surgery and radiation therapy to clear the cancer cells. The further breast cancer progresses, the greater the combination of therapies the patient needs. These therapies may include surgery, chemotherapy, hormone therapy, and radiation therapy. Surgery The doctor can recommend a different type of surgery based on the size & location of cancer, size of the breast. Image Credit: https://medizzy.com/feed/6090735 Lumpectomy: The surgeon removes cancer tissue and leaves a small amount of healthy tissue behind. In the U.S., about 25 percent of women need additional surgery after a #lumpectomy. Image Credit: Biomedical Optics Express Vol. 12, Issue 5, pp. 2647-2660 (2021) Researchers are working to build a medical device that can perform optical coherence tomography (OCT) on excised breast tissue in the operation room and feed imaging data into an AI engine to detect cancer cells. The real-time feedback can help the surgeon determine if more tissue needs to be removed, thus reducing the possibility of additional surgeries in the future. Mastectomy: The surgeon removes the breast tissue (including the skin and nipple) and the tissues that cover the chest muscles. Modified radical mastectomy: Rare procedure to remove the entire breast, many lymph nodes under the arm, the lining of the chest muscles, and, in some cases, the chest wall muscles. Breast reconstruction: Some patients undergo breast reconstruction after mastectomy. Autologous breast reconstruction with a deep inferior epigastric artery perforator (DIEP) flap has become an integral component of the holistic treatment of breast cancer patients. A combination of 3D printing and Artificial intelligence is being experimented with to augment breast reconstruction surgery. Sometimes results of breast reconstruction are disappointing. The CINDERELLA (Comparing patient’s decision on aesthetic outcome with the BCCT.core objective evaluation after controlled teaching in patients proposed for breast cancer locoregional treatment) project aims to create a gold standard method for the aesthetic evaluation by giving patients a better insight into the outcomes, allowing them to judge more objectively, also using inputs from both objective and subjective factors. Machine learning is also being used to determine patient satisfaction post-reconstruction surgery. Chemotherapy uses drugs that stop the growth of cancer cells. A person can receive chemotherapy drugs orally or via injection into the vein or muscle. Machine-learning algorithms are now used to determine the fewest, smallest doses that could shrink the cancer cells, thus reducing the toxic side effects of chemotherapy. Image Credit: Khademhosseini Laboratory Researchers now use biomedical sensors combined with artificial intelligence to monitor and adjust chemotherapy treatment. Hormonal therapy blocks cancer cells from getting the #hormones they need to grow. AI is now effectively used to personalize hormone therapy using the chemical composition of the cancer tissue. Image Credit: https://blog.einstein.ai/receptornet/ ReceptorNet uses advanced machine learning algorithms to determine estrogen receptor status without the need to use an IHC stain. It learns to assign high attention weights to tiles in the H&E image that are the most important for decision-making and to assign low attention weights to tiles that are insignificant for this task. The presence or absence of estrogen receptors would help doctors determine the course of therapy. Image Credit: https://doi.org/10.6004/jnccn.2020.7554 Immunotherapy works with your body’s immune system to help it fight cancer cells or to control side effects from other cancer treatments. Machine learning has vastly improved cancer immunotherapy. Image Credit: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsb.2021.02.007 Artificial Intelligence is used in many ways in immunotherapy. ML classification algorithms are used to characterize cancer cells, which helps determine accurate immunotherapy for breast cancer patients. ML algorithms are used to predict immunotherapy scores, thus increasing the chance of successful cancer immunotherapy. Radiation therapy uses high-energy X-rays to kill cancer cells. External radiation therapy (EBRT) uses a machine to send radiation to the affected area of the body. Internal radiation therapy (brachytherapy) uses a radioactive substance in needles that the surgeon places near the cancer tissue. Image Credit: The Breast, Volume 49, February 2020, Pages 194-200
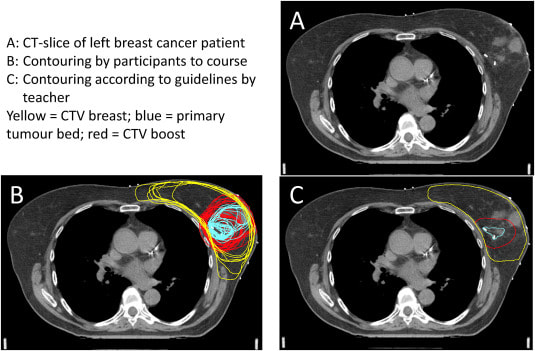
Artificial intelligence is being effectively used to individualize radiation therapy for breast cancer. Deep learning algorithms use neural networks to identify and generate contouring patterns to be combined with information from multiple sources to generate volumes of CT images that can subsequently be validated for RT dose planning by the physician. Big data and advancements in AI are poised to improve breast cancer treatment. Precision therapy and non-invasive surgeries improve the patient survival rate and recovery after the treatment. References
Comments are closed.
|
Page HitsAuthorArchita Archives
January 2023
Categories |

 RSS Feed
RSS Feed